India losing $ 1-2 tn of natural capital every year
Kamal Bawa on India’s Biodiversity
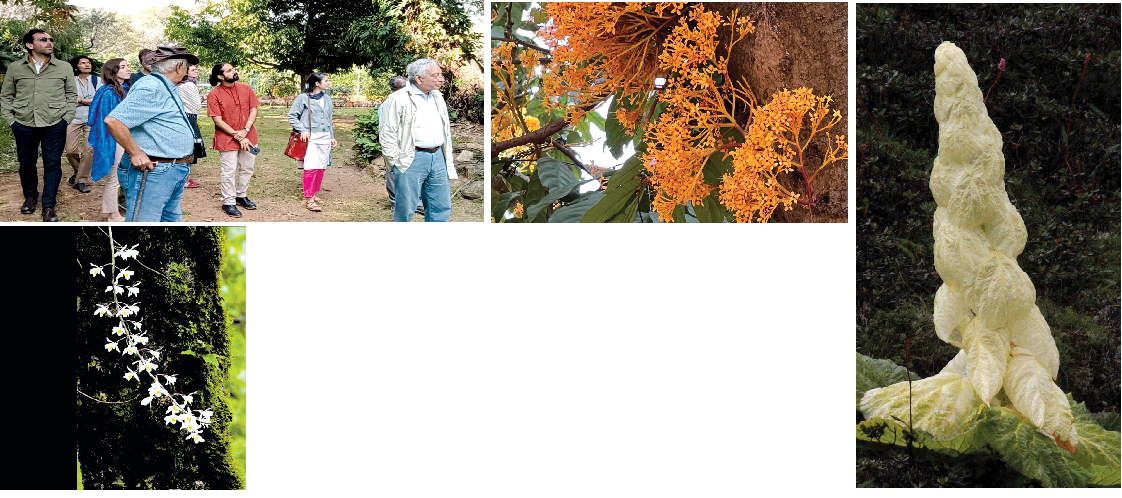
M. A. Siraj / NT: Conservation biologist Professor Kamal Bawa delivered the second Vijay Thiruvady Memorial Lecture on January 12, 2025 at the Bangalore International Centre on "Our incredible Inheritance: India's Plant Wealth. Dr. Bawa is associated with the University of Massachusetts, Boston,(US) and is a past president of Ashoka Trust for Research in Ecology and the environment (STREE), Bangalore. Vijay Thiruvady, an architect by training and profession and a botanist by choice led hundreds of Nature enthusiasts on Lal Bagh Walk on every weekend for over 18 years.
He passed away on August 1, 2023. The BIC has been hosting the Thiruvady Memorial Lecture for the last two years. Here are the excerpts: Our plant wealth is declining very rapidly. We know very little about what the country possesses. India's biodiversity makes India one among the 17 megadiverse countries. But we don't realise that plants are building stones for the ecosystem. If the building collapses, nothing will be left. The country harbours between 16 to 17 thousands of plant species. Though India's geographical area constitutes only 2 per cent of the land area of the globe, it harbours 8 per cent of the world’s biodiversity. Four of the 36 global hotspots of global diversity are in India. Similarly, the country is ranked among the one Vavilov's eight centers of crop diversity. J. D. Hooker, a contemporary of Charles Darwin, wrote seven volumes on biodiversity of India. India has 350 species of Impatience genus. Impatiens is a large, broadly distributed genus of flowering plants in the family Balsaminaceae.
85 per cent of its species are found in the western Western Ghats. Some of these species are found nowhere else in the world. In the same vein, 120 species of Rhododendron are native of eastern Himalayas. But it is a sad reality that India ranks 176 out of 180 countries on the Global Nature Conservation Index in 2024. We also need to be aware that forests are lifeline for Adivasis. They have spiritual connection with forests. We need to recognise the rights of forest dwellers as forests provide livelihood to them. Around 30 per cent of land area of India is affected by degradation. The nation has lost 2.3 million hectares of tree cover during the past three decades which coincide with the economic liberalisation. Seventy per cent of India's rivers are heavily polluted. We are losing one to two trillion dollars of natural capital very year while there is a need to enhance it by $ 4-5 trillion every year. The ATREE took up the conservation efforts on five key verticals, viz Exploration, Restoration, Population and Community Ecology, Botanical Gardens and Research Centers and Plant Information System. It was instrumental in discovering species like Henckelia arunachalensis, Lysionotus namchoomii and Aeschynanthus chayangtajuensis.
I. H. Burkills discovered Hopea shingkeng in Sian Valley of the Himalayas which has never been reported elsewhere. It was considered extinct based on subsequent survey. In terms of restoration, our approach has been based on rigorous research, technology adoption, policy engagement, robust monitoring and evaluation. The ATREE adopted right based approach to forest restoration and management. It also worked with forest dwelling communities in enabling them to have sustainable harvest of fruits like amla, pepper, coffee and has helped 850 families associated with value-added harvest. Saplings of these fruit trees were distributed among 600 families, their women were trained to set up micro-nurseries, and organised sale of surplus production for livelihood diversification.
Our plant wealth and its decline
- Pathways to conserve and restore our natural heritage (based on work at ATREE)
- Concluding remarks
India’s Plant Wealth: Biodiversity
- Unique biodiversity – among the 17 megadiverse countries
- Plant species: about 16,000, possibly 17,000 species
- 2% of global land area – about 8% of biodiversity
- 4 of the 36 global biodiversity hotspots n One of Vavilov’s 8 centers of crop diversity
Biodiversity: Decline
- India’s ranking in biodiversity conservation
- Forest Survey of India
Decrease in dense and increase in open forest: ATREE is engaged in Exploration and Cnservation, Restoration, Sustainable Livelihoods, and Climate Adaptation. It has conservation centres in BR HIlls, Vembanad, MM Hills and Eastern Himalayas. It has produced 45 Ph.Ds, 900 environmental leaders; discovered 100 new species and restored land rights on 196,000 hactares of land.
Restoration across India's Ecosystems: n 30% of land area affected by degradation,
- 2.3 million hectares of tree cover loss
- 40% of India’s wetlands have been lost in the past three decades,
- 70% of India's rivers are heavily polluted
- In 2024 Global Nature Conservation Index, India ranked 176 out of 180 countries, labelled among the worst performers.
Why does conservation matter? India’s goal for 2047 is to be a developed economy with a GDP of $30T.
- India has 8% of the global biodiversity, which approximates about $15 T biocapacity based on today’s estimates.
- The world is losing 3%-5% of natural capital per year.
- To achieve the 2047 goal, India needs to increase its natural capital to over $40 Trillion rapidly.
 English daily published in Bengaluru & Doha
English daily published in Bengaluru & Doha